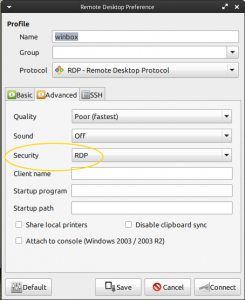
Seems like default settings stopped working and the default RDP needed to be set for Windows 7 to connect properly.
Last logons to Unix Machine
Refer: http://linux.die.net/man/1/last
Enter this command:
$ last | more
Update Ubuntu to See Android Phone
Refer: http://askubuntu.com/questions/463015/ubuntu-14-04-and-android-cant-see-phone-on-my-computer
$ sudo apt-get install mtpfs
Open here terminal in Ubuntu
Refer: http://askubuntu.com/questions/602234/is-it-possible-to-open-a-terminal-in-the-current-directory
Run sudo apt-get install nautilus-open-terminal in a terminal, followed by nautilus -q to quit all open nautilus windows. When nautilus is next opened, a line saying open in terminal should appear in the right click menu.
Please note that the package nautilus-open-terminal is in the universe repositories.
Checking / Pinging a Port
Ports are a concept of UDP and TCP. Ping messages are technically referred to as ICMP Echo Request and ICMP Echo Reply which are part of ICMP. ICMP, TCP, and UDP are "siblings"; they are not based on each other, but are three separate protocols that run on top of IP. Therefore you can not ping a port. What you can do, is use a port scanner like nmap.
$ nmap -p 80 mruckman.com
You can also use:
$ telnet mruckman.com 80
It will give an error if the port is closed or filtered
---
telnet 10.194.55.47 11222
nmap -p 11222 10.194.55.47
$ nmap -p 11222 10.194.55.47
Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-07-08 06:09 PDT
Nmap scan report for haldevcache01.hq.halw.com (10.194.55.47)
Host is up (0.23s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
11222/tcp open unknown
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.60 seconds
# Sign onto server itself
$ netstat -ntpl | grep 11222
Rename files in Linux
Here's how I use rename:
rename 's/search/replace/' *
And here's it in action:
oli@bert:~/Desktop/rawr$ ls
pie\u333.sh
oli@bert:~/Desktop/rawr$ rename 's/\\u333/PIE/' *
oli@bert:~/Desktop/rawr$ ls
piePIE.sh
Installing NPM and NodeJS in Ubuntu
Possible Solution (Not Tested):
http://www.hostingadvice.com/how-to/install-nodejs-ubuntu-14-04/
Updating NPM
Refer: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/23393707/how-to-update-npm
This will update npm using npm itself:
# This is for initial installation
$ sudo npm install npm -g
# This is for upgrade
$ sudo npm update npm -g
From article: If you are stuck, try sudo npm update npm -g. All credit goes to Tim Castelijns. I have tested it on ubuntu 14.04, npm 1.3.10
Note that if you are using nvm for managing multiple versions in your local dev environment for e.g. testing purposes, all your installed versions (listed by nvm ls) are in ~/.nvm, hence you just omit system wide installation (i.e. omit sudo):
$ npm install npm -g
Updated version of NodeJS - Chris Lea
Refer: https://nodesource.com/blog/chris-lea-joins-forces-with-nodesource
Improve Battery Life in Ubuntu
Refer: http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/easily-increase-battery-life-tlp-linux/
Ubuntu
In Ubuntu, you’ll want to do the following:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install tlp tlp-rdw
If you are on a ThinkPad, you’ll need to install a few more packages for maximum battery life, which you can do with the command sudo apt-get install tp-smapi-dkms acpi-call-tools.
# Start the service, only needs done once, will start automatically on boot-up
$ sudo tlp start
Installing Splunk
Go to Splunk.com, and download the 64-bit version of the Linux *.deb
Install through the software center.
Start with the following command:
$ sudo /opt/splunk/bin/splunk start
In the browser, load the portal here: http://127.0.0.1:8000/
Installing MongoDB Ubuntu14.04 and Specific Version of MongoDB
Installing MongoDB in Ubuntu
Refer: http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/tutorial/install-mongodb-on-ubuntu/
Import Public Key
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 7F0CEB10
Create a list file for MongoDB
$ echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu "$(lsb_release -sc)"/mongodb-org/3.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.0.list
### NOTE !!! We need this repository for 2.6.3 installation ###
$ echo 'deb http://downloads-distro.mongodb.org/repo/ubuntu-upstart dist 10gen' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/10gen.list
Reload local package database
$ sudo apt-get update
Install MongoDB packages
Either latest - STOP - Do you want latest?
$ sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org
or Specific version
$ sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org=2.6.3 mongodb-org-server=2.6.3 mongodb-org-shell=2.6.3 mongodb-org-mongos=2.6.3 mongodb-org-tools=2.6.3
Pin a specific version of MongoDB.
Although you can specify any available version of MongoDB, apt-get will upgrade the packages when a newer version becomes available. To prevent unintended upgrades, pin the package. To pin the version of MongoDB at the currently installed version, issue the following command sequence:
$ echo "mongodb-org hold" | sudo dpkg --set-selections
$ echo "mongodb-org-server hold" | sudo dpkg --set-selections
$ echo "mongodb-org-shell hold" | sudo dpkg --set-selections
$ echo "mongodb-org-mongos hold" | sudo dpkg --set-selections
$ echo "mongodb-org-tools hold" | sudo dpkg --set-selections
Versions of the MongoDB packages before 2.6 use a different repo location. Refer to the version of the documentation appropriate for your MongoDB version.
Run MongoDB
The MongoDB instance stores its data files in /var/lib/mongodb and its log files in /var/log/mongodb by default, and runs using the mongodb user account. You can specify alternate log and data file directories in /etc/mongod.conf. See systemLog.path and storage.dbPath for additional information.
If you change the user that runs the MongoDB process, you must modify the access control rights to the /var/lib/mongodb and /var/log/mongodb directories to give this user access to these directories
Start MongoDB.
Issue the following command to start mongod:
$ sudo service mongod start
Verify that the mongod process has started successfully by checking the contents of the log file at /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log for a line reading
[initandlisten] waiting for connections on port <port>
where <port> is the port configured in /etc/mongod.conf, 27017 by default.
$ sudo service mongod status
Stop MongoDB.
As needed, you can stop the mongod process by issuing the following command:
sudo service mongod stop
Restart MongoDB.
Issue the following command to restart mongod:
$ sudo service mongod restart
Keeping it from auto-starting:
Refer: http://edgar.tumblr.com/post/3242138398/disable-start-of-a-service-on-boot-in-ubuntu
/etc/init/mongod.conf
ENABLE_MONGOD="yes" -> "no"
Using RoboMongo
Name: localhost
Address: localhost:27017
Removing MongoDB
Refer: http://askubuntu.com/questions/497139/how-to-completely-uninstall-mongodb-2-6-3-from-ubuntu-13-04
$ sudo dpkg -l | grep mongo
That should output a list of packages with mongo in the name.
If there are still files left on the system following an apt-get remove mongo, try and run the command again with the --purge switch, using a wildcard search for the name:
Such as, but review the above command, you will probably need to customize this:
$ sudo apt-get remove mongodb* --purge
Real Example on Ubuntu 14.04
$ sudo apt-get remove mongodb-org mongodb-org-mongos mongodb-org-server mongodb-org-shell mongodb-org-tools --purge